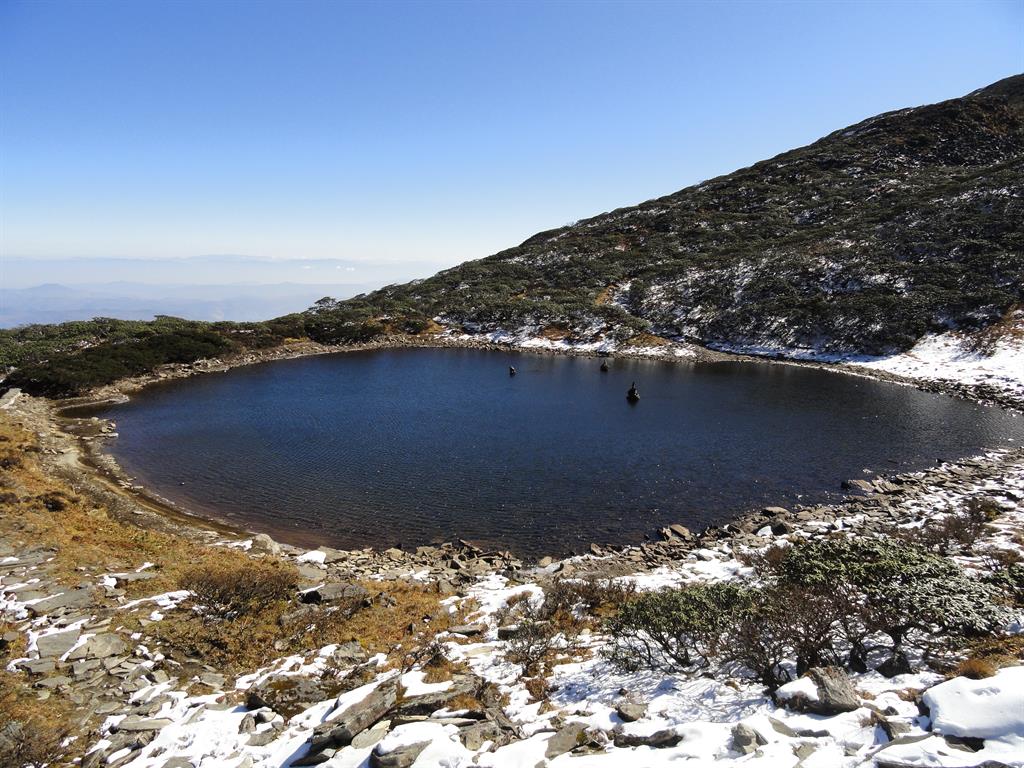
中国大理苍山世界地质公园位于云南省白族自治州大理市境内,面积933 平方千米,由苍山、洱海和山麓平原三个景观组成。地质遗迹包括构造形迹、岩石地貌、冰川地貌和水体景观;构造形迹有褶皱、变形、断裂等;岩石地貌从板岩、片岩到片麻岩、变粒岩、千枚岩、大理岩、角闪岩、混合岩、碎裂岩、糜棱岩等,种类多达十余种,堪称变质岩的博物馆。冰川地貌主要分布于海拔2800 米以上的苍山之上,有角峰、刃脊、冰斗、冰窖、冰蚀谷、冰蚀湖、冰碛、冰碛堤、冰坎等微地貌组合。
大理苍山是一部孕育了近20 亿年的“天然地质史书”,特殊的地质、地理、地貌造就了山水相映,风、花、雪、月、石共存的自然景观组合,当地世居少数民族与其和谐共处,形成了一幅优美的自然风景画卷。
Celebrating Earth Heritage
Dali-Cangshan UNESCO Global Geopark is located in China’s Yunnan province. Dali-Cangshan UNESCO Global Geopark is located in the central section of the Bai Nationality Autonomous Prefecture, including Dali City, Yangbi County and Eryuan County.Located in western Yunnan Province at the southern end of the lofty Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Mount Cangshan is a young mountain formed only 50 million years ago. However, the rocks that make up the mountain are more than 2 billion years old. Mount Cangshan is mainly composed of metamorphic rocks, including marble renowned for its beautiful colour and structure. It is the southernmost mountain in Asia reached by the latest glaciation period and many glacial landforms are well preserved and displayed.
Sustaining local Communities
Mount Cangshan is a sacred mountain and displays unusual natural beauty. The unique and colourful traditions of the Bai indigenous people have helped make the site a popular tourist destination.
The UNESCO Global Geopark prepared a Geopark’s master plan, and hosted the 2015 Chinese UNESCO Global Geopark annual conference. A number of universities and a number of research institutions established a research and education partnership with the UNESCO Global Geopark. They have published geoscience books and leaflets, produced popular science postcards and videos. Local community residents benefit from geotourism, and promote the sustainable development of local economic, social and ecological environment.